Ever wondered how QR code scanners instantly recognize complex patterns — even under harsh lighting or from different angles?
Behind that effortless scan lies a sophisticated system of precision optical components working in perfect harmony.
From checkout counters and warehouses to healthcare and transport systems, QR code scanners are everywhere — and their speed, accuracy, and adaptability depend heavily on the quality of their optical design.

The Core Optical Components of QR Code Scanners
1. Lens Systems: Convex and Compound Lenses

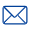
At the heart of the scanner lies the lens system, often utilizing aspherical or compound lenses to minimize optical aberrations such as spherical and chromatic distortions. These lenses ensure crisp image focus and clarity across varying distances — from close-range retail checkouts to extended warehouse shelf scans.
Application Example: In logistics, scanners must read QR codes on shelves at various heights. Autofocus lens systems enable seamless adjustment, maintaining sharp image quality throughout the scan range.
2. Filters: Infrared Cut-Off & Bandpass Filters
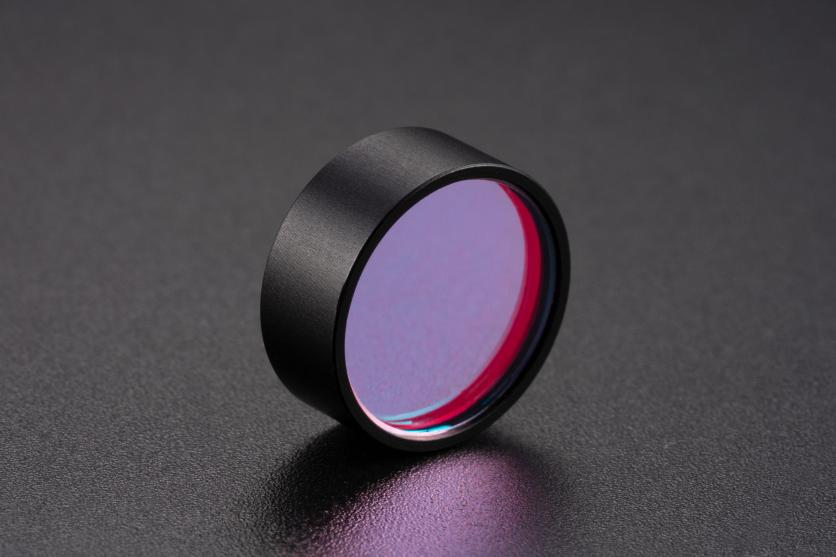

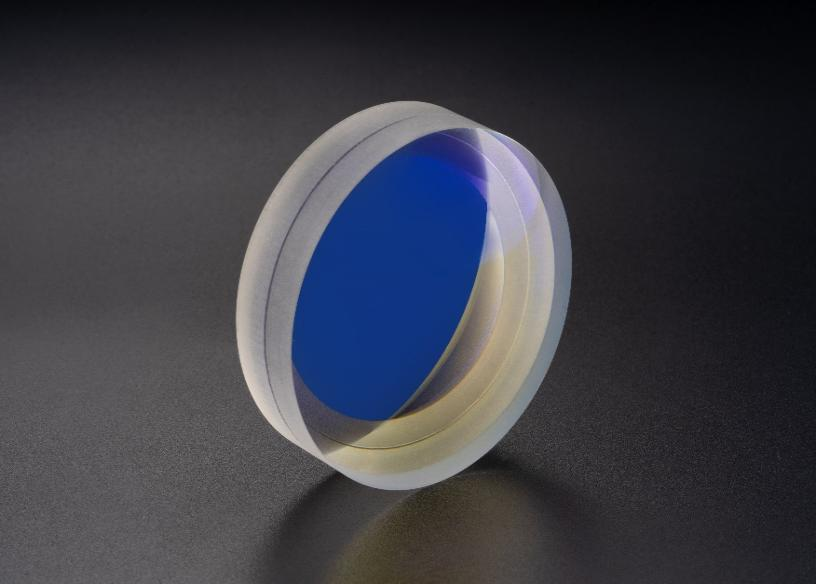
To enhance signal clarity, QR code scanners incorporate specialized optical filters. An infrared cut-off filter blocks IR light (e.g., from sunlight) to prevent sensor overexposure and color shifts, while a bandpass filter selectively transmits light at specific wavelengths — often matched to red LED light (~650 nm) — for optimal contrast and reduced noise.
Application Example: In outdoor retail kiosks or courier pickups, filters minimize ambient light interference, preserving the sharp black-and-white contrast of the QR code under bright conditions.
3. Mirrors & Beam Splitters: Compact Optical Path Design
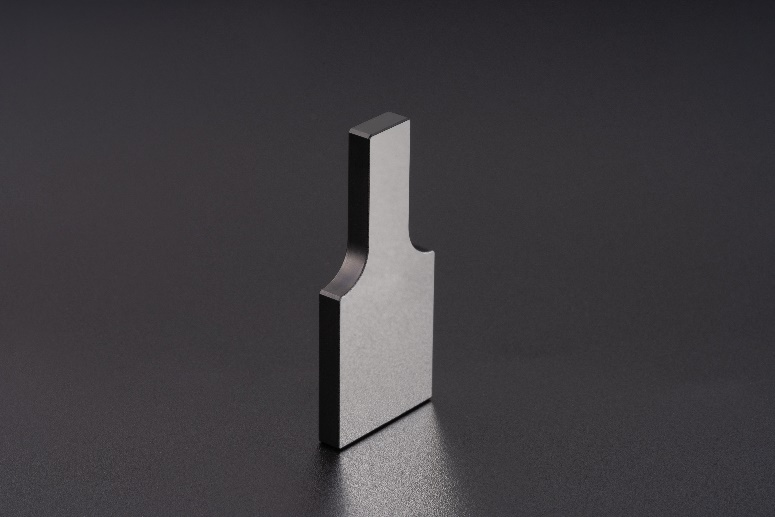

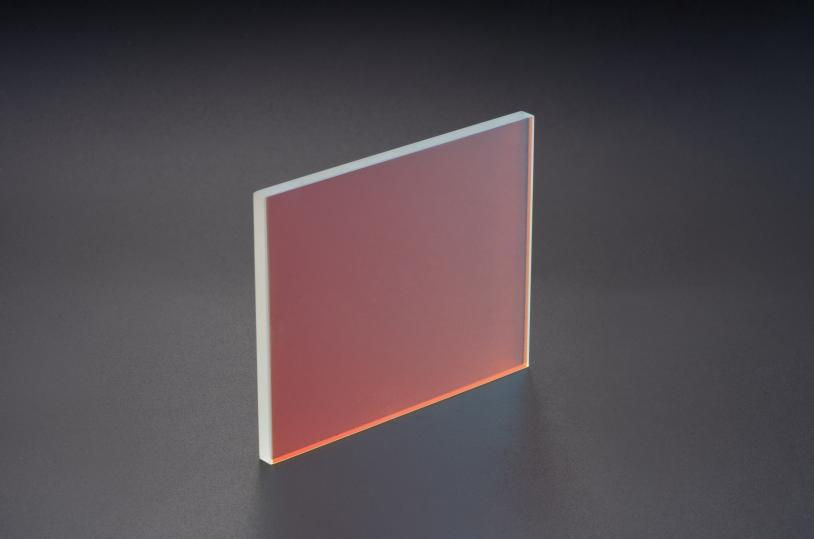
Mirrors are used to fold the optical path, enabling compact scanner designs without sacrificing focal length. Beam splitters separate the illumination and imaging paths, reducing interference and improving overall system efficiency.
Application Example: In ATMs or embedded POS systems, mirrors allow the scanner to function within limited internal space while maintaining a long optical range.
Future Trends in Optical Design for Scanners
1. Super Depth-of-Field Lenses
Advanced technologies such as liquid lenses and adaptive apertures allow continuous focusing from a few millimeters to over a meter, enabling one-touch scanning in dynamic environments.
2. Multispectral Imaging
By integrating UV or IR imaging, scanners can detect invisible QR codes or read through translucent packaging materials — ideal for security and pharmaceutical applications.
3. AI-Powered Optical Tuning
Real-time algorithms can now adjust exposure, gain, and white balance dynamically, optimizing image acquisition in complex lighting or fast-moving environments.
The Foundation of Intelligent Scanning
Precision optical components are truly the “eyes” of QR code scanners. Their design and integration directly determine the device’s speed, accuracy, and ability to adapt to environmental challenges. As optical engineering continues to merge with AI and IoT technologies, QR code scanners are evolving into smarter, more adaptive tools across every industry.
At Jiujon Optics, we remain at the forefront of this evolution — delivering high-performance optical solutions that enable the next generation of intelligent vision systems.
Post time: Jun-05-2025